Kitchen - Tip Question: How Long Can Cooked Beans Be Stored in the Fridge?
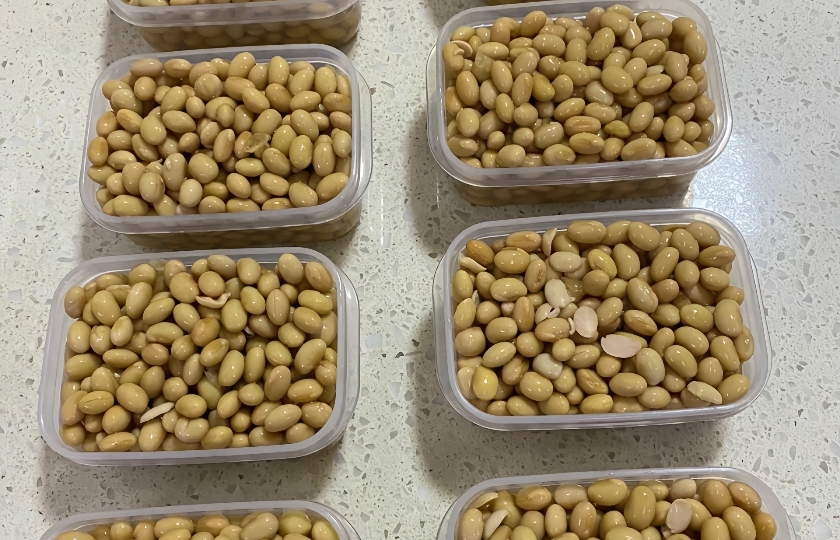 Beans are a great addition to a healthy diet, and they taste even better when cooked. I often cook extra beans and store them in the fridge for later use. But recently, I started wondering—how long can cooked beans actually last in the fridge? Let's dive into this topic together!
Beans are a great addition to a healthy diet, and they taste even better when cooked. I often cook extra beans and store them in the fridge for later use. But recently, I started wondering—how long can cooked beans actually last in the fridge? Let's dive into this topic together!
How long do cooked beans keep in the refrigerator?
The storage duration of cooked beans in the fridge depends on several factors. Generally, if you store them properly in an airtight container in the refrigerator, they can last for about 3-5 days. The fridge's temperature, typically between 32-40°F (0-4°C), slows down microbial growth but doesn't stop it completely.
If you freeze the beans, they can last for several months, although their texture might become a bit mushy after thawing.
The type of beans also affects the storage time. Smaller beans like mung beans might start to degrade after about 3 days in the fridge, while larger beans like fava beans can last up to 5 days under the same conditions.
Tips for Storing Cooked Beans
Clean and Seal Properly: Make sure the beans are clean and stored in an airtight container. If the beans were contaminated before storage or the container isn't sealed well, they might spoil in less than two days.
Signs of Spoilage: Spoiled beans will have an off smell, mold, or a slimy texture. If you notice any of these signs, it's best to discard them.
How Long Can Cooked Beans Last Without Refrigeration?
If you don't refrigerate cooked beans, their storage time is influenced by several factors:
Environmental Temperature
Room Temperature (68-77°F / 20-25°C): Cooked beans can last for about 1-2 days at room temperature. During spring or fall, beans cooked at noon might still be good the next day, but they could start to develop a slight sour smell.
Higher Temperatures (Above 77°F / 25°C): In hotter conditions, like during summer when room temperatures reach 86°F (30°C) or higher, beans can spoil in as little as half a day. High temperatures provide an ideal environment for microbial growth, causing beans to sour, discolor, and spoil quickly.
Bean Condition and Storage Container
Initial Quality: If the beans weren't properly cooked or were contaminated before cooking, they will spoil faster at room temperature. For example, beans with residual mold spores can quickly go bad.
Storage Container: Storing beans in an open bowl exposes them to air and microbes, accelerating spoilage. Using a covered container can help slow down the process but won't be as effective as refrigeration.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your cooked beans stay fresh and safe to eat for as long as possible.
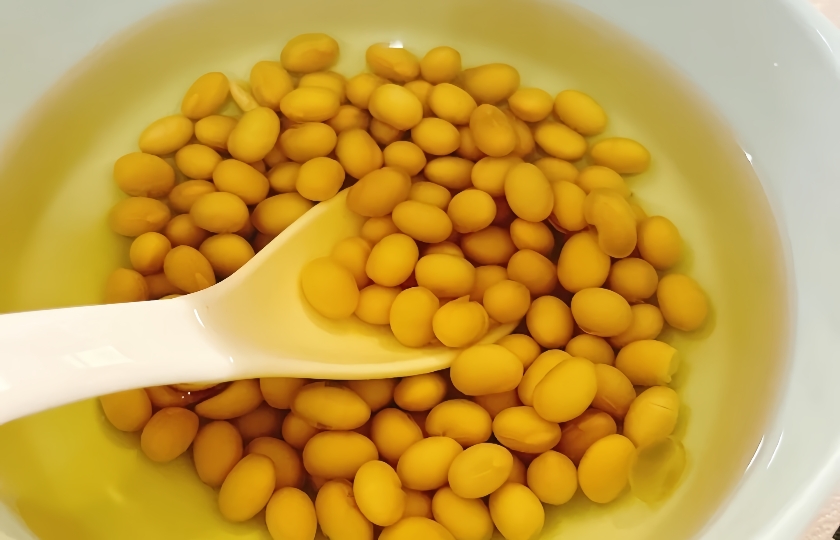

Why Aren’t My Cooked Beans Soft?
If your cooked beans aren’t softening, it could be due to several reasons:
Bean Variety and Quality
Type of Bean: Different types of beans have varying textures and cooking times. Some heirloom or less processed varieties, like wild black beans, have thicker skins and require longer cooking times.
Age and Storage: Old beans or those stored improperly can become dry and hard. If they’ve been exposed to moisture, they might develop mold, which can damage their structure and make them difficult to soften.
Cooking Conditions
Cooking Time: Beans like red beans may need 1-2 hours to soften. Insufficient cooking time will leave them hard.
Water Amount: Beans need enough water to absorb and soften. Ensure the water level is 1-2 inches above the beans.
Cooking Temperature: Low heat may not transfer enough energy to soften beans efficiently. Using a pressure cooker can speed up the process.
Other Factors
Thick Skins: Beans like chickpeas have thick skins that can hinder water absorption. Removing some skins or soaking them in warm water before cooking can help.
Acidic Ingredients: Adding acidic ingredients like lemon juice or vinegar can harden beans’ cell walls, making them difficult to soften. Avoid adding these until the beans are cooked.
How to Tell if Cooked Beans Have Spoiled?
To determine if cooked beans have spoiled, consider the following:
Appearance
Color: Freshly cooked beans should have an even color. If you see black spots, white fuzz, or discoloration, they’re likely spoiled. For example, green beans should be vibrant; if they turn black or have white mold, they’re bad.
Shape: Spoiled beans may become shriveled or mushy, losing their plumpness. Red beans, for instance, may shrink when spoiled.
Smell
Aroma: Fresh beans have a mild, pleasant smell. If they emit a sour, rancid, or rotten odor, they’ve likely spoiled due to bacterial growth.
Texture
Feel: Use a spoon or chopsticks to gently touch the beans. Fresh beans should be firm and elastic. If they’re sticky, slimy, or fall apart easily, they might be spoiled. For example, spoiled soybeans might turn mushy and break apart easily.
By keeping these tips in mind, you can ensure your beans are cooked to perfection and safe to eat!
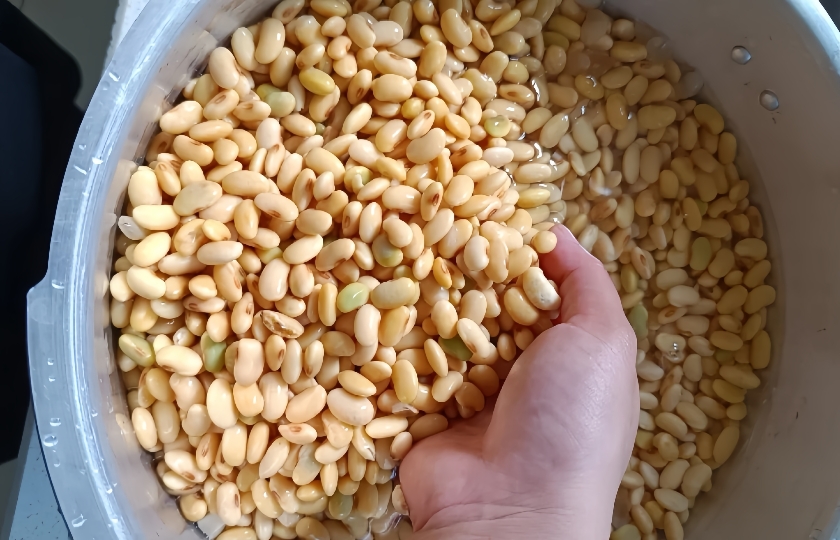

Should I Add Baking Soda to Beans?
Adding baking soda to beans can be a matter of personal preference and specific cooking goals. Here are some considerations:
Benefits of Adding Baking Soda
Faster Cooking: Baking soda is an alkaline substance that can help break down the cell walls of beans, making them cook faster and become softer. For example, adding a small amount of baking soda when cooking red beans or green beans can significantly reduce the cooking time and result in a softer texture.
Improved Texture: Beans cooked with baking soda tend to have a creamier and softer texture, which can be desirable in certain dishes.
Drawbacks of Adding Baking Soda
Nutrient Loss: The alkaline environment created by baking soda can degrade some vitamins in the beans, such as B vitamins.
Flavor Impact: Using too much baking soda can impart a soapy or bitter taste to the beans, which might not be pleasant.
When to Avoid Baking Soda
Preserving Flavor and Nutrition: If you want to maintain the beans' natural flavor and nutritional integrity, it might be best to avoid using baking soda. For example, when making traditional dishes like black bean cake that highlight the natural flavor of black beans, it's better not to use baking soda.
Delicious Dishes with Cooked Beans?
Cooked beans can be transformed into a variety of delicious dishes. Here are some ideas:
Bean Pastes
Red Bean Paste (Anko): Cooked red beans can be mashed into a paste. Add sugar and a bit of oil, then cook on low heat until smooth. This paste can be used in:
Red Bean Buns: Soft, fluffy buns filled with sweet red bean paste.
Mooncakes: Red bean paste combined with salted egg yolks for a rich, flavorful filling.
Red Bean Spring Rolls: Crispy on the outside and soft on the inside.
Soups and Stews
Bean Soups: Cooked beans can be used to make hearty soups and stews.
White Bean and Pork Rib Soup: White beans cooked with pork ribs, resulting in a rich, meaty broth.
Green Bean Soup: Cooked green beans with rock sugar and lily bulbs, a refreshing summer dessert soup.
Sweet Bean Soup: Cooked kidney beans with red dates and longan, a nourishing and delicious dessert.
Salads
Bean Salads: Cooked beans can be mixed with fresh vegetables for nutritious salads.
Black Bean Salad: Black beans with lettuce, purple cabbage, and cherry tomatoes, dressed with olive oil, vinegar, and a touch of honey.
Chickpea Salad: Chickpeas mixed with cucumber and bell peppers, seasoned with salt and black pepper, for a colorful and flavorful dish.
By exploring these methods and recipes, you can make the most of your cooked beans and enjoy a variety of tasty and nutritious meals!